Tuesday, November 20, 2012
Real World Project
We made the majority of the tutorial videos in todays lesson. Community Clips isn't very user friendly but once you can figure out how to get it working it is relatively easy to use.
Thursday, November 15, 2012
Real World Project-Finished
The part of our assignment that is being marked for our progress mark is uploaded on our Studentnet site.
The theory component of our assignment is done as are most of the 'How-to" video tutorials.
We still need to complete the voice-overs that will be put with the videos to describe what is taking place on the screen. These voice-overs have not been completed due to lack of the equipment needed such as microphones. This is proving to be a problem as the videos that were created by community clips are all done but we can't finish the assignment without the voice-overs. A few more microphones may have to be purchased to overcome this problem.
The theory component of our assignment is done as are most of the 'How-to" video tutorials.
We still need to complete the voice-overs that will be put with the videos to describe what is taking place on the screen. These voice-overs have not been completed due to lack of the equipment needed such as microphones. This is proving to be a problem as the videos that were created by community clips are all done but we can't finish the assignment without the voice-overs. A few more microphones may have to be purchased to overcome this problem.
Wednesday, November 7, 2012
Real World Project
Diyomira and Drishti spent todays lesson creating the stop motion video that will be our example to show the younger students.
I worked mainly on the theory component of the assignment and downloaded community clips onto my computer so we can start making the tutorials next lesson.
I worked mainly on the theory component of the assignment and downloaded community clips onto my computer so we can start making the tutorials next lesson.
Tuesday, November 6, 2012
Real World Project
For my groups Real World Project we are doin a stop motion video and a series of tutorial videos to explain how to create the video.
My group consists of Diyomira, Drishti and myself.
We have created the stop motion video and have done multiple of the tutorial videos
My group consists of Diyomira, Drishti and myself.
We have created the stop motion video and have done multiple of the tutorial videos
Tuesday, October 9, 2012
Tools for Schools Research Task
Evernote: Evernote is a type of software
designed for notetaking and archiving. A "note" can be a piece of
text, a webpage or webpage excerpt, a photograph, a voice memo, or a
handwritten "ink" note. Notes can also have file attachments. These
notes can be sorted into folders, then tagged, annotated, edited, given comments,
searched and exported as part of a notebook.
Screenshots:  |
| Evernote Logo |
 |
| Evernote Page |
Evernote clients are available for Microsoft Windows, Mac OS
X, Android, iOS (iPhone, iPad, iPod Touch), Windows Mobile, Windows Phone, BlackBerry,
and Google Wave platforms. There are portable versions of Evernote available
for flash drives and U3 drives.
A viable competitor for Evernote is Microsoft OneNote.
Microsoft OneNote: Microsoft OneNote is a computer
program for information gathering and multi-user
collaboration. It can gather users' notes (handwritten or typed), drawings,
screen clippings, and audio commentaries and share them with other users of
Microsoft OneNote over the Internet. Notes can also be edited from a web
browser.
OneNote is available
as an application for Windows, iOS, Android, Windows Phone, and Symbian.
OneNote has multiple (But less regarded) competitors. These
include Evernote, Yojimbo, Springpad, Simplenote Circus Ponies NoteBook and Zotero.
Google+: Google+ is a multilingual social networking and
identity service. Google+ includes social services such as Google Profiles, and
introduces new services such as Circles, Hangouts and Sparks.
Screenshots:
 |
| Gooogle+ Logo |
Google+ is an
internet site allowing it to be available on any platform with internet access.
The major
competitor for Google+ is Facebook.
Tuesday, September 4, 2012
Assignment- Game Finished
My program that I have made in scratch is finished and works to the desired extent. It would've been good if I could change the background colour but as my images all have white backgrounds it would have looked silly.
The game detirmines whether you have won, lost or have drawn with the computer. To start again you press the space bar. The image below is the result of my pick being paper and the computer picking scissors. Sprite 1 then 'says'
The game detirmines whether you have won, lost or have drawn with the computer. To start again you press the space bar. The image below is the result of my pick being paper and the computer picking scissors. Sprite 1 then 'says'
 |
| The image above is the result of my pick being paper and the computer picking scissors. Sprite 1 then 'says' lost due to scissors beating Paper. |
Tuesday, August 28, 2012
Assignment
I've decided to make my project using Scratch, App Inventor was to slow and highly unreliable.
With Scratch I'm making a Rock, Paper, Scissors game. The person starts the game and is told to click on what hand position (rock, paper or scissors) they want to use. The computer will randomly generate its own hand position and it will determine whether you won or lost.
With Scratch I'm making a Rock, Paper, Scissors game. The person starts the game and is told to click on what hand position (rock, paper or scissors) they want to use. The computer will randomly generate its own hand position and it will determine whether you won or lost.
Sunday, August 12, 2012
Basic Drums
Today i was working on the app inventor guides task, specifically the Basic Drums task. The WIFI was especially slow today so loading evereything took ages....... Especially finding a drum sound.
Sunday, July 29, 2012
Augmented Reality
1. Define augmented reality (AR).
Augmented reality (AR) is the technology of combining real word images, video, etc. with computer-generated information and/or imagery
2. Provide some examples of how augmented reality might be used.
-Picking furniture
-Finding Places/ Find out out street names
-Interactive Prints
-Update on social network
-Happenings around you
3. Traditionally a user would use text entry to search for information in say Maps or a search engine. How does AR offer a different alternative?
AR allows the user to use their actions to find the infomation. Pointing the AR at the direction will give you certain infomation about it. It uses a filter search so you can find specific infomation.
AR allows the user to use their actions to find the infomation. Pointing the AR at the direction will give you certain infomation about it. It uses a filter search so you can find specific infomation.
4. How might the following people make use of AR;
● A mechanic
"ARMAR, or Augmented Reality for Maintenance and Repair, is a head mounted display unit that provides graphic overlays to assist you in making repairs. An Android phone provides an interface to control the graphics you view during the process. Published in IEEE, and recently tested with the United States Marine Corps on an armored turret, ARMAR can cut maintenance times in half by guiding users to the damaged area and displaying 3D animations to demonstrate the appropriate tools and techniques."
"ARMAR, or Augmented Reality for Maintenance and Repair, is a head mounted display unit that provides graphic overlays to assist you in making repairs. An Android phone provides an interface to control the graphics you view during the process. Published in IEEE, and recently tested with the United States Marine Corps on an armored turret, ARMAR can cut maintenance times in half by guiding users to the damaged area and displaying 3D animations to demonstrate the appropriate tools and techniques."
● An interior decorator
It can be used to demonstrate what a certain furnish would appear like in a room and what an ideas can look like when the room is completed.
It can be used to demonstrate what a certain furnish would appear like in a room and what an ideas can look like when the room is completed.
● A student
Sunday, July 15, 2012
Flowchart Symbols
1. What is a flowchart?
A flowchart is a visual representation that illustrates the sequence of operations to be performed to get the solution of a problem.
2.Describe the basic flowchart symbols for;
3. With the decision making symbol (diamond) and the process symbol (rectangle), what are the rules for how many lines may enter and leave the symbol.
With the decision making symbol one arrow enters the box but multiple (normally two) can leave. With the process symbol one arrow enters and leaves the box.
4. Study the sample flowcharts then create a flowchart for a coin toss where heads means Mary pays for the pizza and Tales means Bill pays.
- Example.
- SUM is a variable
- Essentially before 'N' it really says 'let N equal 0'.
What is an Algorithm
1. boil the water,
2. place coffee in the cup,
3. place sugar in the cup,
4. add the boiling water,
5. add milk,
6. stir.
1.Specific
2.correct sequence
Swapping steps would change th end product and this case it wouldn't work at all.
Define Algorithms for the following processes.
| Posting a letter. | Making toast. | Calling a friend on the phone |
Thursday, June 28, 2012
Sunday, June 3, 2012
Data Compression
1. Name two programs used for file compression.
-WinZip
-Stuffit
-WinZip
-Stuffit
What name is given to the file compression method that looks for redundant patterns?
Why can’t music be compressed efficiently with this type of compression technique?
What method of compression is most suited to graphics and music files?
Name compressed file formats for the following media; music, still graphics, audio and video.
Wednesday, May 23, 2012
Basic HTML
How to create:
-Headings
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
-Background colours
<body style="background-color:yellow">
-Paragraph break
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
<p>This is another paragraph.</p>
-Line break
<p>This is<br />a para<br />graph with line breaks</p>
-Bold font
<!-- This is a comment -->
Colours and codes for HTML
-Headings
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
-Background colours
<body style="background-color:yellow">
-Paragraph break
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
<p>This is another paragraph.</p>
-Line break
<p>This is<br />a para<br />graph with line breaks</p>
-Bold font
<b>
Comments <!-- This is a comment -->
Change Font and color
<h1 style="font-family:verdana;">A heading</h1>
<p style="font-family:arial;color:red;font-size:20px;">A paragraph.</p>
</body>
<p style="font-family:arial;color:red;font-size:20px;">A paragraph.</p>
</body>
The text on your page must be used to explain;
Colours and codes for HTML
| Color | Color HEX | Color RGB | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #000000 | rgb(0,0,0) | ||||||||||
| #FF0000 | rgb(255,0,0) | ||||||||||
| #00FF00 | rgb(0,255,0) | ||||||||||
| #0000FF | rgb(0,0,255) | ||||||||||
| #FFFF00 | rgb(255,255,0) | ||||||||||
| #00FFFF | rgb(0,255,255) | ||||||||||
| #FF00FF | rgb(255,0,255) | ||||||||||
| #C0C0C0 | rgb(192,192,192) | ||||||||||
| #FFFFFF | rgb(255,255,255) |
Monday, May 21, 2012
Using Frontpage
Using http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/frontpage-help/overview-RZ001114106.aspx?section=1.
1. What two steps are recommended in planning your site?
-Planning your site structure with sketches
-Planning your site layout again with sketches.
2. What is a web server?
A Web server is a computer that runs special serving software. That software "serves" HTML pages and associated files when requested by a client, such as a Web browser.
3. Provide examples of some features that FrontPage Server Extensions provide for a website?
Design element Interactives
Security- Log in.
Allows direct uploads and downloads of data and files
4. How do you put your website on a web server?
To put your site on a Web server, you publish it. Publishing generally means copying all of the files to a remote location on a server. In most cases, the remote location is either an HTTP path or an FTP path. The path you use depends on what technologies your server supports.
5. FrontPage has two key functions – website design and management
6. What are some commonly used file names for Home Pages accepted by servers?
7. What is FrontPage Metadata and which two folders contain these files?
FrontPage metadata is information about your FrontPage Web site that makes managing the site possible.
The folders are the _vti_cnf folder and the _vti_pvt folder.
8. There are two basic types of website can you create in FrontPage; what are they and how do they differ?
Disk-Based and Sever-Based.
A disk-based site is a FrontPage Web site you create on your local hard disk and then later publish to a Web server. A server-based site is one you create and work with directly on a Web server, without the extra step of publishing.
Wednesday, May 16, 2012
Internet Addresses
1. What is a URL?
Uniform (or universal) resource locator, the address of a World Wide Web page.
2. What is an IP address and how is it related to a URL?
The browser communicated with a name server to translate the server name "www.google.com.au" into an IP Address,
which it uses to connect to the server machine. The browser then formed
a connection to the server at that IP address on port 80.
3. Given our school website's URL is http://www.mcauley.nsw.edu.au, what is our domain
name and what protocol do you need to use to access the site?
Protocol: 'http' (hypertext transfer protocol)
4. In the context of an IP address, what is an octet?
IP stands for Internet protocol, and these addresses are 32-bit numbers, normally expressed as four "octets" in a "dotted decimal number." The four numbers in an IP address are called octets because they can have values between 0 and 255,
Broadband
Speedtest
For a bit of fun determine the speed of our
internet connection using the site below. Start by testing the connection speed
to the Sydney
location then select a different location from the map (drag the map to find a
location).
Home Computer = 0.50 Mbps
1. What is meant by upload
and download speeds?
Uploading involves sending a copy of a file from a computer to a remote network connection; for instance, Web developers and publishers upload files to their Web server to make them available for other people to access.
Uploading involves sending a copy of a file from a computer to a remote network connection; for instance, Web developers and publishers upload files to their Web server to make them available for other people to access.
Downloading involves the reception of a file that has been
uploaded to a remote network. Often this refers to a person copying a
file from a remote network to her personal computer; for example, people
download music from iTunes after they make a purchase.
Upload speed is usually slower than download speed because Internet
providers have designed their systems to optimize download speeds. This
is because most Internet users spend more time downloading than
uploading. In other words, Internet providers give priority to
downloading since it's more frequently done than uploading
Mbps (mega bits per second) or Kbps (Kilo bits per second)
3. Why do different locations offer different download speeds? Hint: “bottleneck”
There are various reasons for different speeds:
- cables, they type of material used,optic fibre- copper wire-whether the server is wireless
-crowds/No. of users eg townhouse
-Amount of data being uploaded/downloaded
-Bottleneck- Size of channels/branches
-The weather can affect some wireless channels
-Time of day
-Usage
 |
| 'Bottlenecks' reduces the room data has to travel therefore reducing the speed it is transmitted at. |
Sunday, May 13, 2012
- How did the internet originate?
The interenet was first created in 1968 in America. In 1957 a remote connection had to be developed so the people could work on the computers despite the fact that they had to be stored in a cold room. At the same the idea of 'time-sharing' came up allowing multiple users to work on one computer. They created a system where knowledge could be transfered faster. Universities were cautious about letting others use their computers so they had a smaller computer, commonly termed the 'Interface' which took over control of network activities. The IMP's connected to other interfaces called the Network Control Protocol. This was later replaced by the more efficent TCP 'Transmission Control Protocol". The NPL Network was expected to support many users and file transfer. The idea that files should be split up came in to play to avoid 'congestion'. This was called packet switching. Upon discovery of a possible atomic bomb attack they created a "de-centralised' network so that if a station was hit the network wouldn't be destroyed. The creation of the french CYCLADES was another milestone. They (with their low budget) had to focus on connecting with other networks.
TCPIP Transmission control protocol internet protocol.Who were the people most responsible for creating it?The Internet was originally created by DARPA (the Defence Advanced Research Projects Agency) as a means of sharing information on defence reseacrh between involved universities and defence research facilities.The internet was not created by a single person, however here are some people who made large contributions:
ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network).
- The idea-Leonard Kleinrock'sPeople such as- Elmer Shapiro, Steve Carr, Steve Crocker, Jeff Rulifson, Ron Stoughton, Paul Baran, Thomas Marill, Lawrence Roberts, Barry Wessler, Bolt Beranek and Newman, Inc. (BBN)
What system immediately preceded the internet? What was its purpose?
Lee had actually begun networking computers before the development of the PC, with his Community Memory project in the late 1970s. This system had terminals (like computer screens with keyboards connected to one large computer that did the processing). These were placed in laundromats, the Whole Earth Access store, and community centres in San Francisco. This network used permanent links over a small geographical area rather than telephone lines and modems.
What is an IP packet? What is it comprised of?IP packet is the basic data chunk that can be sent over the Internet. All the data is partitioned into IP packets on the sending computer and reassembled on the receiving computer. Each packet contains header information that includes the type of traffic it is (FTP or UDP, for example) and where it originated from.
What does TCP stand for? How does TCP deal with lost IP packets?
Transmission Control Protocol over Internet Protocol. These are two transmission protocols that work together to help the servers, clients and devices on the network talk to one another.Why do computer people like everything in letters?They may prefer it because acronyms are easier to remember, as well as shorter to type and refer to.
Sunday, April 1, 2012
Some Key Terms- Internet and Web Design
- Define the term - Protocol:When computers communicate with each other, there needs to be a common set of rules and instructions that each computer follows. A specific set of communication rules is called a protocol.
- What are the following protocols used for?
TCP/IP: Stands for "Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol." These two protocols were developed in the early days of the Internet by the U.S. military. The purpose was to allow computers to communicate over long distance networks.
http: Stands for "HyperText Transfer Protocol." This is the protocol used to transfer data over the World Wide Web. That's why all Web site addresses begin with "http://". Whenever you type a URL into your browser and hit Enter, your computer sends an HTTP request to the appropriate Web server.
SMTP: Stands for "Simple Mail Transfer Protocol." This is the protocol used for sending e-mail over the Internet. Basically, SMTP is a set of commands that authenticate and direct the transfer of electronic mail.
POP: Stands for "Post Office Protocol." "POP" is a simple, standardized method of delivering e-mail messages. A POP mail server receives e-mails and filters them into the appropriate user folders.
FTP: Stands for "File Transfer Protocol." It is a common method of transferring files via the Internet from one computer to another.
- What does GUI stand for? What was used before GUI? Stands for "Graphical User Interface". It refers to the graphical interface of a computer that allows users to click and drag objects with a mouse instead of entering text at a command line. The graphical user interface was first introduced to the public by Apple with the Macintosh in 1984. However, the idea was actually taken from an earlier user interface developed by Xerox. Early dynamic information devices such as radar displays, where input devices were used for direct control of computer-created data, set the basis for later improvements of graphical interfaces.
4. There are two methods of data transmission – serial and parallel. Explain the difference between them.
Serial transmits data one bit at a time as it only is connected by one wire whereas parallel transmits anything up to a byte at a time if connected by 8 wires.
5. Define the term “URL”. Explain the components that make up the url.
- Stands for "Uniform Resource Locator". A URL is the address of a specific Web site or file on the Internet. A URL is used when a Web client makes a request to a server for a resource. A URL for HTTP (or HTTPS) is normally made up of three or four components:
- A scheme. The scheme identifies the protocol to be used to access the resource on the Internet. It can be HTTP (without SSL) or HTTPS (with SSL).
- A host. The host name identifies the host that holds the resource. For example, www.example.com. Host names can also be followed by a port number. Well-known port numbers for a service are normally omitted from the URL. Most servers use the well-known port numbers for HTTP and HTTPS , so most HTTP URLs omit the port number.
- A path. The path identifies the specific resource within the host that the Web client wants to access.
- A query string. If a query string is used, it follows the path component, and provides a string of information that the resource can use for some purpose (for example, as parameters for a search or as data to be processed). The query string is usually a string of name and value pairs, for example, q=bluebird.
6. In the context of data transmission, what is “error detection”?
It is simply the searching for an detection of any errors that may have occurred in the sending of data
It is simply the searching for an detection of any errors that may have occurred in the sending of data
7. Why would error detection be important for the internet
8. Name and explain one common method of error detection.
The oldest method of error correction involves using parity. It works by adding an additional bit to each character word transmitted. The state of the bit is determined by a number of factors such as the type of parity and the number of logic-one bits in the data character.

*A parity bit is a bit that is added to ensure that the number of bits with the value one in a set of bits is even or odd. Parity bits are used as the simplest form of error detecting code.
The oldest method of error correction involves using parity. It works by adding an additional bit to each character word transmitted. The state of the bit is determined by a number of factors such as the type of parity and the number of logic-one bits in the data character.

*A parity bit is a bit that is added to ensure that the number of bits with the value one in a set of bits is even or odd. Parity bits are used as the simplest form of error detecting code.
9. What is HTML and explain why it is important
- HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language; HTML is not a programming language, it is a markup language. HTML is what formats web pages. It is used in conjunction with JavaScript and CSS to make the page you see. It is used to format the text, layout, images, links, etc. The combination of these three elements has come to be known as XHTML.
Monday, March 12, 2012
To get a Paramter Query to open in form view
As with every other task the worksheet was designed to suit microsoft 2003 therefore meaning that i spend most of time trying to figure out where various buttons have disapeared to.
Through editing the worksheet, it is now (once I've finished!) easier to understand. The task requires a few various steps to reach the rquired point.
After creating the menu form and setting it as the opening page you can add a button that opens a parameter query.
Through editing the worksheet, it is now (once I've finished!) easier to understand. The task requires a few various steps to reach the rquired point.
After creating the menu form and setting it as the opening page you can add a button that opens a parameter query.
Sunday, March 4, 2012
Creating A parameter query
Parameter queries are useful to find infomation quickly and efficiently.
To create the parameter query use have to:
-Create a query using query design and chose the fields you want to be shown.
-In the criteria box paste
To create the parameter query use have to:
-Create a query using query design and chose the fields you want to be shown.
-In the criteria box paste
LIKE [Enter the first character to search by: ] & "*"The infomation shown in the brackets is what the parameter query asks.-The created query when opened will ask using the parameter query what value you require. eg A for any record that starts with 'A'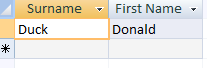 |
| Using "D" |
Tuesday, February 28, 2012
Adding Buttons to a form
This is a very difficult process to decipher as it the task itself was done through 2003 Access. Through playing around with buttons we were eventually able to complete the task.
The buttons enable the database to be easier to navigate. They enable ease of use and make certain tasks easier.
Clicking on the created button "photo" in access takes us to the form containing their ID photo.
I further created a button on this form so I can return to the button page.
The buttons enable the database to be easier to navigate. They enable ease of use and make certain tasks easier.
Clicking on the created button "photo" in access takes us to the form containing their ID photo.
I further created a button on this form so I can return to the button page.
Monday, February 27, 2012
Adding Sound to a form
The process of adding a sound to a database follows the same process as adding an image.
-Create a field and rename it
-Set data type to OLE object
-Right click and click on insert object
-Click on create from file
-Use browse to find your sound file and click ok
-After this process the file should show up in your database
-Create a form using form wizard
-The sound file should be in place in the form
-Create a field and rename it
-Set data type to OLE object
-Right click and click on insert object
-Click on create from file
-Use browse to find your sound file and click ok
-After this process the file should show up in your database
-Create a form using form wizard
-The sound file should be in place in the form
Sunday, February 19, 2012
Social Issues Related to databases
In our group we have Krozina, Diyomira and myself.
We are researching Identity fraud.
I am doing questions 2 and 5.
We are researching Identity fraud.
I am doing questions 2 and 5.
Bits and Bytes
What is a digit?
A digit is a single place that can hold numerical values between 0 and 9. Digits are normally combined together in groups to create larger numbers.
A digit is a single place that can hold numerical values between 0 and 9. Digits are normally combined together in groups to create larger numbers.
2. “normal” counting numbers used in everyday life a based on what sequence of numbers? The binary number system
3. Where does the word bit originate from?
The word 'bit' was derived from the term binary digit (0 and 1).
4. Binary numbers don’t use base 10. What base do they use? What digits are available in base 2?
Binary numbers use base two. The digits it uses are 0 and 1.
- Examine the tables below
Base 10
Place Value | 10 000 | 1 000 | 100 | 10 | 1 |
Place Value | 104 | 103 | 102 | 101 | 100 |
Digit | 9 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 2 |
Digit Value | 90 000 | 0 | 300 | 0 | 2 |
90 302 (base 10) = (9 x 10000) + (3 x 100) + (2 x 1)
If 6,357 can be written as;
(6 * 1000) + (3 * 100) + (5 * 10) + (7 * 1) = 6000 + 300 + 50 + 7
Ø How would you write 4,321
(4*1000)+(3*100)+(2*10)+(1*1)
- Examine the table below
Base 2
Place Value | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
Place Value | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 |
Digit | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Digit Value | 16 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
10100 (base 2) = (1 x 16) + (1 x 4) = 20 (base 10)
Ø Write the following numbers in binary (base 2)
21
24
30
- What is a byte?
A group of binary digits or bits (usually eight) operated on as a unit.
- How many bytes in a kilo, mega, giga and tera bytes.
Kilo: 1024 bytes
Mega: 1 048 576 bytes
Giga: 1 073 741 824 bytes
Tera: 1 099 511 627 776 bytes
- Complete the following conversions;
1000 Mb = 0.9765625Gb
500 Gb = 512000Mb
5000 Kb = 4.88281Mb
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)